This video demonstrate Omental patch repair with peritoneal lavage is the mainstay of treatment for perforated peptic ulcers in many institutions. Laparoscopic repair has been used to treat perforated peptic ulcers since 1990, but few randomized studies have been carried out to compare open versus laparoscopic procedures.
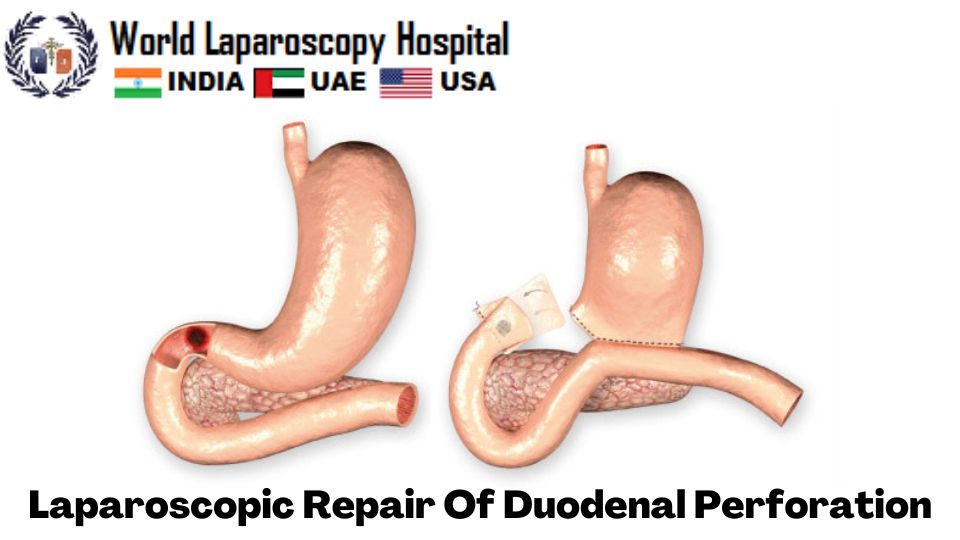
aparoscopic repair of duodenal perforation is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that involves repairing a hole or tear in the duodenum, which is the first part of the small intestine. The procedure is performed using a laparoscope, a thin, flexible tube with a camera and light source that is inserted through a small incision in the abdomen.
During the procedure, the surgeon identifies the site of the perforation and cleans the surrounding area. The edges of the perforation are then carefully aligned and sutured together to close the hole. In some cases, a patch may be used to reinforce the repair.
The benefits of laparoscopic repair of duodenal perforation include smaller incisions, less pain, a shorter hospital stay, and faster recovery time compared to traditional open surgery. However, this procedure may not be suitable for all patients, depending on the severity and location of the perforation.
As with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks and complications associated with laparoscopic repair of duodenal perforation, including bleeding, infection, and injury to nearby organs. It is important to discuss the risks and benefits of this procedure with your healthcare provider to determine if it is the right choice for you.
The advantages of laparoscopic repair of duodenal perforation include:
-
Minimally invasive: Laparoscopic repair of duodenal perforation is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that involves smaller incisions compared to traditional open surgery. This results in less trauma to the surrounding tissues and muscles, leading to less pain, scarring, and a faster recovery time.
-
Reduced hospital stay: Patients who undergo laparoscopic repair of duodenal perforation typically experience a shorter hospital stay compared to traditional open surgery. This means that patients can return to their daily activities sooner and can avoid the risks associated with a prolonged hospital stay.
-
Lower risk of complications: Laparoscopic repair of duodenal perforation is associated with a lower risk of complications such as infections, bleeding, and injury to nearby organs. This is due to the smaller incisions and more precise surgical techniques used during the procedure.
-
Faster recovery: Patients who undergo laparoscopic repair of duodenal perforation typically experience a faster recovery time compared to traditional open surgery. This means that they can resume their normal activities sooner, including eating and drinking.
-
Better cosmetic outcomes: The smaller incisions used during laparoscopic repair of duodenal perforation result in better cosmetic outcomes compared to traditional open surgery. This is because there is less scarring and a shorter recovery time, which leads to a more aesthetically pleasing result.
-
Lower risk of adhesions: Laparoscopic repair of duodenal perforation is associated with a lower risk of adhesions, which are bands of scar tissue that can form between abdominal organs after surgery. Adhesions can cause chronic pain, bowel obstruction, and other complications.
-
Better visualization: The laparoscope used during the procedure provides the surgeon with a magnified view of the surgical site, allowing for better visualization and more precise surgical techniques. This can lead to better outcomes and a lower risk of complications.
-
Reduced blood loss: Laparoscopic repair of duodenal perforation is associated with reduced blood loss compared to traditional open surgery. This can reduce the need for blood transfusions and other interventions to manage bleeding.
-
Reduced risk of hernias: The smaller incisions used during laparoscopic repair of duodenal perforation are associated with a reduced risk of hernias, which can occur when tissue or organs protrude through weakened or damaged abdominal muscles.
Overall, laparoscopic repair of duodenal perforation is a safe and effective procedure that offers many advantages over traditional open surgery. However, it is important to discuss the risks and benefits of this procedure with your healthcare provider to determine if it is the right choice for you.
While laparoscopic repair of duodenal perforation is generally considered safe and effective, there are potential risks and complications associated with the procedure. These can include:
-
Bleeding: There is a risk of bleeding during the procedure or after surgery, which may require blood transfusions or additional surgical intervention.
-
Infection: Any surgical procedure carries a risk of infection, which can occur at the surgical site or in other parts of the body. Antibiotics may be prescribed to prevent or treat infections.
-
Injury to nearby organs: There is a small risk of injury to nearby organs such as the liver, pancreas, or stomach during the procedure, which may require additional surgery to repair.
-
Anesthesia complications: General anesthesia is required for the procedure, which carries its own set of risks such as allergic reactions, breathing problems, or heart complications.
-
Intestinal leakage: In rare cases, the repaired duodenal perforation may leak, leading to abdominal infections or other complications.
-
Adhesions: Although laparoscopic surgery is associated with a lower risk of adhesions than open surgery, some patients may still develop adhesions, which can cause chronic pain, bowel obstruction, or other complications.
-
Hernia: There is a risk of hernia formation at the site of the incision or in other parts of the abdomen.
It is important to discuss the risks and benefits of laparoscopic repair of duodenal perforation with your healthcare provider to determine if the procedure is right for you. Your surgeon will take steps to minimize the risk of complications, but it is important to understand that no surgical procedure is completely risk-free.
| Older Post | Home | Newer Post |





