Laparoscopy Hysterectomy
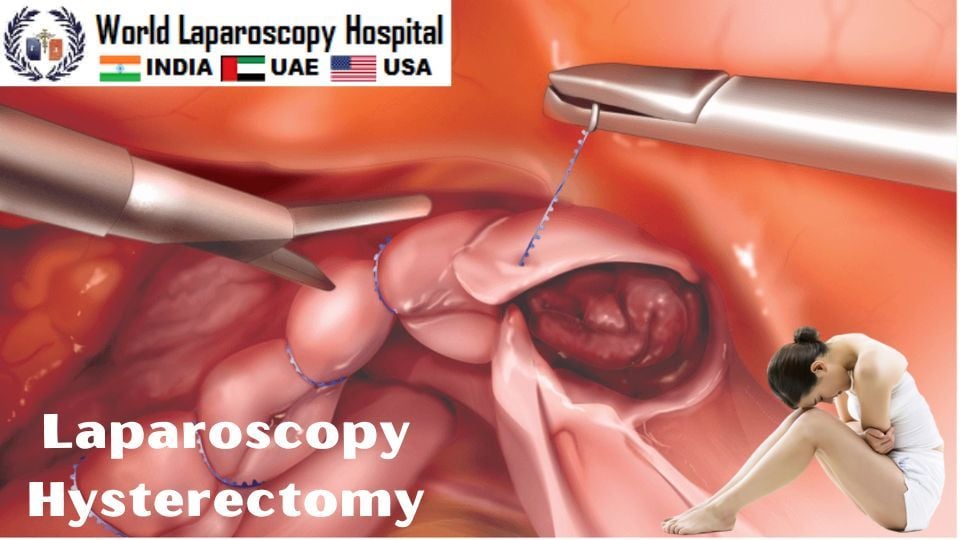
This video demonstrates laparoscopic hysterectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure to remove the uterus. A small incision is made in the belly button and a tiny camera is inserted. The surgeon watches the image from this camera on a TV screen and performs the operative procedure.
Laparoscopic hysterectomy is a surgical procedure in which the uterus is removed using laparoscopic techniques, which involve making small incisions in the abdomen and using specialized surgical instruments and a camera to view the internal organs. The procedure is less invasive than traditional open surgery and typically results in less pain, scarring, and recovery time.
During a laparoscopic hysterectomy, the surgeon may remove the uterus alone or may also remove the ovaries and fallopian tubes, depending on the reason for the surgery and the patient's needs. The procedure can be performed under general anesthesia, and most patients are able to go home the same day or the day after the surgery.
As with any surgery, there are potential risks and complications associated with laparoscopic hysterectomy, including bleeding, infection, damage to surrounding organs, and anesthesia-related problems. However, these risks are generally lower with laparoscopic surgery than with traditional open surgery.
Laparoscopic hysterectomy is typically recommended for women with conditions such as fibroids, endometriosis, or heavy menstrual bleeding that have not responded to other treatments. However, the procedure may not be suitable for all patients, and a thorough evaluation by a qualified healthcare provider is necessary to determine whether laparoscopic hysterectomy is the right option for a particular individual.
Laparoscopic hysterectomy offers several advantages over traditional open surgery, including:
Smaller incisions: Laparoscopic surgery requires only a few small incisions, typically less than 1 cm in length, compared to the larger incision required for open surgery. This results in less scarring, less pain, and a shorter recovery time.
Reduced blood loss: The use of laparoscopic techniques can reduce the amount of bleeding during surgery, which may lead to a faster recovery and reduce the need for blood transfusions.
Faster recovery time: Because laparoscopic surgery is less invasive, patients often experience less pain and can resume normal activities more quickly than with open surgery.
Shorter hospital stay: Most laparoscopic hysterectomies are performed on an outpatient basis or require only a short hospital stay, compared to several days or more with open surgery.
Better visualization: The use of a camera and specialized surgical instruments allows the surgeon to have a clearer view of the internal organs, which may result in better surgical outcomes.
Reduced risk of complications: Laparoscopic surgery is associated with a lower risk of infection, blood clots, and other complications than open surgery.
Preserves surrounding tissue: Laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive technique that allows the surgeon to work around the uterus and other organs without damaging surrounding tissue. This means that patients may experience less pain, scarring, and recovery time than with open surgery.
Lower risk of hernia: Because laparoscopic surgery involves smaller incisions, there is a lower risk of developing a hernia, which is a protrusion of tissue or an organ through the abdominal wall.
Lower risk of adhesions: Adhesions are bands of scar tissue that can form after surgery and cause organs to stick together. Because laparoscopic surgery is less invasive, there is a lower risk of developing adhesions than with open surgery.
Improved cosmetic results: The smaller incisions used in laparoscopic surgery typically result in less scarring and a better cosmetic outcome than traditional open surgery, which can leave a larger scar.
Lower risk of infection: Laparoscopic surgery involves smaller incisions and reduced exposure to the environment, which may result in a lower risk of infection than with open surgery.
Less pain and discomfort: Laparoscopic surgery is associated with less pain and discomfort than traditional open surgery. This can lead to improved quality of life during the recovery period.
Quicker return to normal activities: Patients who undergo laparoscopic hysterectomy typically experience a quicker return to normal activities than those who undergo open surgery. This can be particularly important for women who have busy lives and cannot afford a prolonged recovery period.
Reduced need for pain medication: Because laparoscopic surgery is less invasive and associated with less pain, patients may require less pain medication during the recovery period.
Improved patient satisfaction: Patients who undergo laparoscopic hysterectomy are often more satisfied with their surgical experience and outcomes than those who undergo traditional open surgery. This can be attributed to the reduced pain, shorter recovery time, and improved cosmetic results associated with laparoscopic surgery.
Overall, laparoscopic hysterectomy is a safe and effective alternative to traditional open surgery for many women. However, it is important to discuss the potential risks and benefits of this procedure with a qualified healthcare provider to determine whether it is the best option for an individual patient.
Laparoscopic hysterectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the uterus through small incisions made in the abdomen. As with any surgery, there are risks and potential complications associated with laparoscopic hysterectomy. Some of the possible complications include:
Infection: There is a risk of infection with any surgery, including laparoscopic hysterectomy. Antibiotics are typically given before and after the surgery to reduce the risk of infection.
Bleeding: There may be some bleeding during or after the surgery. In some cases, a blood transfusion may be necessary.
Damage to nearby organs: During the surgery, there is a risk of damage to nearby organs such as the bladder, ureters, or intestines.
Blood clots: There is a risk of developing blood clots after any surgery, including laparoscopic hysterectomy. This risk can be reduced by moving around as soon as possible after the surgery.
Anesthesia complications: There is a risk of complications related to anesthesia, such as allergic reactions or breathing difficulties.
Pain and discomfort: Pain and discomfort are common after laparoscopic hysterectomy. Pain medications and other treatments can help manage these symptoms.
Delayed healing: It may take several weeks for the incisions to heal completely, and there is a risk of developing a hernia at the incision sites.
Urinary problems: After laparoscopic hysterectomy, some women may experience difficulty with urination or urinary incontinence. These issues may be temporary or may require additional treatment.
Vaginal cuff dehiscence: In rare cases, the incision at the top of the vagina where the uterus was removed may not heal properly and can separate, causing vaginal cuff dehiscence. This can lead to bleeding or infection and may require additional surgery.
Adverse reactions to medication: Some women may experience adverse reactions to medications used during the surgery or for pain management after the surgery.
Emotional and psychological effects: Surgery, including laparoscopic hysterectomy, can have emotional and psychological effects on some women. It is important to discuss any concerns or feelings with your healthcare provider.
Long-term effects: While laparoscopic hysterectomy is considered safe, there may be long-term effects on overall health, including an increased risk of heart disease and other chronic conditions.
Urinary problems: After laparoscopic hysterectomy, some women may experience difficulty with urination or urinary incontinence. These issues may be temporary or may require additional treatment.
Vaginal cuff dehiscence: In rare cases, the incision at the top of the vagina where the uterus was removed may not heal properly and can separate, causing vaginal cuff dehiscence. This can lead to bleeding or infection and may require additional surgery.
Adverse reactions to medication: Some women may experience adverse reactions to medications used during the surgery or for pain management after the surgery.
Emotional and psychological effects: Surgery, including laparoscopic hysterectomy, can have emotional and psychological effects on some women. It is important to discuss any concerns or feelings with your healthcare provider.
Long-term effects: While laparoscopic hysterectomy is considered safe, there may be long-term effects on overall health, including an increased risk of heart disease and other chronic conditions.
It is important to follow your doctor's post-operative instructions carefully and attend all follow-up appointments to monitor your recovery and address any potential complications. If you experience any unusual symptoms or complications after laparoscopic hysterectomy, be sure to contact your doctor immediately.
2 COMMENTS
Dr. Mrunalini Jyotish
#2
Nov 6th, 2023 11:01 am
Laparoscopic hysterectomy is a minimally invasive surgery for uterine removal, using small incisions and a camera. It's less invasive than open surgery, offering reduced pain, scarring, and recovery time.
Dr. Rajlaxmi Sridhar
#1
Aug 27th, 2020 11:16 am
Very good video with a clear and simple explanation! keep up the good work! Thanks for uploading video of Laparoscopy Hysterectomy.
| Older Post | Home | Newer Post |





