Laparoscopic Incisional Hernia Repair by Polyurethane mesh
Add to
Share
296 views
Report
2 months ago
Description
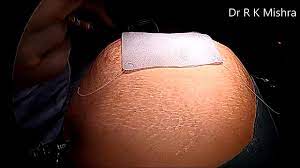
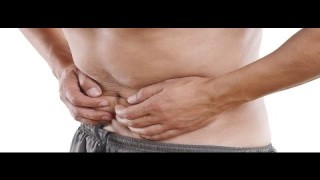
Incisional hernia is a common complication following abdominal surgeries, occurring due to weakness in the abdominal wall at the site of a previous surgical incision. Patients often present with a bulge at the site, discomfort, pain, or even bowel obstruction in severe cases. Over the years, the management of incisional hernias has evolved, and laparoscopic repair has become a widely accepted minimally invasive approach due to reduced postoperative pain, faster recovery, and lower recurrence rates compared to open surgery. Why Laparoscopic Approach? Laparoscopic incisional hernia repair involves the placement of a synthetic mesh through small keyhole incisions using a camera and specialized instruments. Advantages of the laparoscopic approach include: Smaller incisions, resulting in less postoperative pain and faster recovery. Better visualization of the hernia defect and surrounding tissues. Reduced risk of wound infection and seroma formation. Ability to identify and repair multiple defects during the same procedure. Polyurethane Mesh in Hernia Repair Polyurethane mesh is a type of biocompatible synthetic mesh used for hernia repair. It has several benefits over conventional polypropylene or polyester meshes: Flexibility and Strength: Polyurethane mesh is strong yet flexible, allowing it to conform to the abdominal wall while providing durable reinforcement. Reduced Adhesion Formation: Its biocompatible coating minimizes the risk of adhesions to the intestines or other intra-abdominal organs. Lightweight Structure: Being lightweight, it reduces foreign body sensation and chronic pain post-surgery. Enhanced Integration: The mesh encourages tissue ingrowth, providing long-term stability and lowering recurrence rates. Surgical Technique Patient Preparation: General anesthesia is administered, and the patient is positioned to optimize access to the hernia site. Port Placement: Small incisions are made for the laparoscope and working ports. Carbon dioxide is used to create a pneumoperitoneum for better visualization. Hernia Sac Reduction: Adhesions are carefully released, and the hernia sac contents are reduced back into the abdominal cavity. Mesh Placement: The polyurethane mesh is measured, trimmed, and inserted into the abdomen. It is positioned to cover the defect with adequate overlap (usually 4–5 cm beyond the defect margin). Mesh Fixation: The mesh is secured using sutures, tacks, or a combination of both, ensuring it stays flat and stable. Closure: Ports are removed, pneumoperitoneum is released, and incisions are closed. Postoperative Care Patients typically experience less postoperative pain and can resume normal activities faster than with open repair. Early ambulation is encouraged to prevent complications like deep vein thrombosis. Follow-up is necessary to monitor for recurrence or complications such as seroma, infection, or mesh-related issues. Conclusion Laparoscopic incisional hernia repair using polyurethane mesh represents a modern, minimally invasive approach that combines the benefits of laparoscopic surgery with the superior properties of polyurethane mesh. It provides durable repair, minimizes complications, and ensures faster recovery, making it a preferred choice for both surgeons and patients dealing with incisional hernias.
Similar Videos