Emergency Laparoscopic Repair of a Perforated Gastric Ulcer
Add to
Share
183 views
Report
3 weeks ago
Description
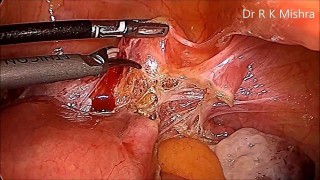
Perforated gastric ulcer is one of the most life-threatening surgical emergencies encountered in general surgery. The condition demands immediate diagnosis and prompt surgical intervention to prevent sepsis, peritonitis, and multi-organ failure. At World Laparoscopy Hospital (WLH), Gurugram, under the expert leadership of Dr. R. K. Mishra, the laparoscopic repair of perforated gastric ulcer is performed with precision, innovation, and excellence — setting a global benchmark for minimally invasive emergency surgery. ? Understanding Perforated Gastric Ulcer A gastric ulcer perforation occurs when an ulcer erodes through the full thickness of the stomach wall, allowing gastric contents to spill into the peritoneal cavity. This leads to chemical peritonitis and rapid bacterial contamination. Patients typically present with sudden, severe upper abdominal pain, rigid abdomen, and signs of shock — a true surgical emergency. ? Laparoscopic Approach: Modern Standard for Emergency Ulcer Repair While open surgery has traditionally been used, the laparoscopic approach offers distinct advantages — less postoperative pain, quicker recovery, shorter hospital stay, and reduced wound complications. At World Laparoscopy Hospital, this life-saving procedure is performed through three to four small keyhole incisions, utilizing advanced HD laparoscopic imaging and energy-based instruments for precision. ? Step-by-Step Laparoscopic Repair Procedure Step 1: Patient Preparation and Positioning After resuscitation and stabilization, the patient is placed in a supine position with slight reverse Trendelenburg to facilitate exposure of the upper abdomen. General anesthesia with nasogastric decompression and Foley catheter insertion are essential steps. Step 2: Port Placement A three-port technique is commonly used: Umbilical port (10mm) for the camera Left upper quadrant (5mm) working port Right upper quadrant (5mm) assistant port In selected cases, a fourth port may be added for better retraction. Step 3: Diagnostic Laparoscopy The peritoneal cavity is inspected to confirm the site of perforation — most often located on the anterior wall of the duodenum or stomach. The degree of peritoneal contamination is assessed, and all quadrants are carefully examined. Step 4: Peritoneal Lavage Thorough peritoneal irrigation with warm saline is performed to remove gastric contents and fibrinous debris. This crucial step prevents postoperative abscess formation and sepsis. Step 5: Identification of the Ulcer Perforation The perforation site is identified, typically ranging between 5–10 mm in diameter. Gentle suction and irrigation help delineate the defect margins clearly. Step 6: Primary Closure of the Perforation The defect is closed using 2-0 absorbable sutures (Vicryl or PDS) in an interrupted or figure-of-eight fashion. Intracorporeal knot tying is performed under magnified vision, ensuring no tension on the edges. Step 7: Omental Patch Reinforcement (Graham Patch) A small tongue of omentum is mobilized and placed over the sutured area, secured with a few interrupted stitches — a technique known as the Graham omental patch. This reinforces the repair and promotes healing. Step 8: Final Lavage and Drain Placement The peritoneal cavity is again irrigated until clear, and a drain is placed in the subhepatic region to monitor postoperative leakage or collection. Step 9: Closure and Recovery Ports are removed under direct vision, and the incisions are closed neatly. The patient is extubated and shifted to recovery for close monitoring. ? Postoperative Care and Recovery At World Laparoscopy Hospital, a well-structured postoperative protocol ensures optimal outcomes: Early ambulation within 24 hours Gradual reintroduction of oral fluids IV antibiotics and proton pump inhibitors Drain removal after 48–72 hours if output is minimal Most patients are discharged within 3–5 days and can resume normal activities soon after. ? Advantages of Laparoscopic Repair at WLH Minimal postoperative pain and scarring Faster recovery and shorter hospitalization Reduced risk of wound infection Comprehensive training and live case demonstration for surgical fellows ? Excellence in Emergency Laparoscopy Training World Laparoscopy Hospital is not just a center for treatment but also a world-renowned training institution. Surgeons from across the globe learn advanced laparoscopic emergency procedures here, guided by Dr. Mishra’s systematic teaching and real-time operative mentorship. Conclusion The laparoscopic repair of perforated gastric ulcer represents a perfect blend of surgical expertise, technology, and emergency precision. At World Laparoscopy Hospital, this critical operation is performed with world-class standards, transforming what was once a high-risk open emergency into a safe, minimally invasive, and rapidly recoverable procedure.
Similar Videos