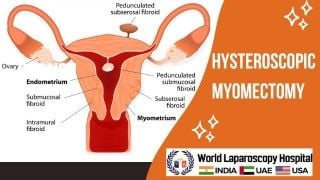
Laparoscopy: Revolutionizing Peritoneal Tuberculosis Diagnosis and Treatment
Add to
Share
923 views
Report
2 years ago
Description
Introduction: Peritoneal tuberculosis is a challenging disease that affects the peritoneum, the thin membrane lining the abdominal cavity. It is a form of tuberculosis that specifically targets the peritoneum and can lead to severe complications if left untreated. Traditional diagnostic methods for peritoneal tuberculosis have often been inadequate, resulting in delayed diagnosis and compromised patient outcomes. However, the advent of laparoscopy has brought about a revolutionary change in both the diagnosis and treatment of peritoneal tuberculosis, offering improved accuracy, efficiency, and therapeutic benefits. Diagnostic Advancements: Laparoscopy, a minimally invasive surgical technique, has significantly transformed the diagnostic landscape of peritoneal tuberculosis. Unlike conventional diagnostic methods such as imaging scans and serological tests, laparoscopy allows direct visualization of the peritoneum, facilitating accurate identification of tuberculous lesions. The laparoscopic approach offers a magnified view of the peritoneal surface, enabling the surgeon to detect subtle abnormalities that may be missed by other diagnostic modalities. The ability to obtain biopsy samples during the procedure further enhances the diagnostic accuracy, as histopathological examination can confirm the presence of tuberculosis granulomas. Advantages in Treatment: In addition to its diagnostic prowess, laparoscopy also plays a pivotal role in the therapeutic management of peritoneal tuberculosis. The laparoscopic approach allows for targeted interventions, such as peritoneal biopsy and adhesiolysis, which are crucial for optimal treatment outcomes. By directly visualizing and accessing the affected areas, surgeons can perform meticulous adhesiolysis, removing the adhesions that may impede the absorption of anti-tubercular drugs. This enhances the effectiveness of drug therapy and improves the overall response to treatment. Furthermore, laparoscopy enables the insertion of intraperitoneal catheters for delivering anti-tubercular medications directly into the peritoneal cavity, leading to enhanced drug concentration at the site of infection. Minimally Invasive Nature: One of the key advantages of laparoscopy in peritoneal tuberculosis is its minimally invasive nature. Traditional open surgery often requires larger incisions, resulting in significant postoperative pain, prolonged hospital stays, and delayed recovery. In contrast, laparoscopy employs small incisions and the use of specialized instruments, leading to reduced surgical trauma, minimal scarring, and faster postoperative recovery. This not only improves patient comfort but also allows for earlier initiation of anti-tubercular treatment, thereby minimizing disease progression and potential complications. This topic explores the groundbreaking impact of laparoscopy on the diagnosis and treatment of peritoneal tuberculosis. Peritoneal tuberculosis is a challenging form of the disease that affects the thin membrane lining the abdominal cavity. Traditional diagnostic methods for this condition have often been inadequate, leading to delayed diagnosis and compromised patient outcomes. However, laparoscopy, a minimally invasive surgical technique, has revolutionized the approach to peritoneal tuberculosis. The essay delves into the advancements brought about by laparoscopy in the field of peritoneal tuberculosis. It highlights how laparoscopy offers improved accuracy and efficiency in diagnosis, enabling direct visualization of the peritoneum and detection of tuberculous lesions. The ability to obtain biopsy samples during the procedure further enhances diagnostic accuracy by confirming the presence of tuberculosis granulomas. Moreover, the essay discusses the therapeutic benefits of laparoscopy in peritoneal tuberculosis. It emphasizes how laparoscopy facilitates targeted interventions such as peritoneal biopsy and adhesiolysis, which are essential for optimal treatment outcomes. By directly visualizing and accessing affected areas, surgeons can remove adhesions that impede the absorption of anti-tubercular drugs, thereby enhancing the effectiveness of drug therapy. The description highlights the minimally invasive nature of laparoscopy, contrasting it with traditional open surgery. It emphasizes the benefits of smaller incisions, reduced surgical trauma, minimal scarring, and faster postoperative recovery. These advantages not only improve patient comfort but also allow for earlier initiation of anti-tubercular treatment, minimizing disease progression and potential complications. Overall, this topic showcases how laparoscopy has transformed the field of peritoneal tuberculosis diagnosis and treatment. It emphasizes the diagnostic accuracy, therapeutic advantages, and minimally invasive nature of laparoscopy, ultimately leading to improved patient care and outcomes in the management of this challenging disease. Conclusion: Laparoscopy has revolutionized the diagnosis and treatment of peritoneal tuberculosis, offering numerous advantages over traditional methods. Its diagnostic accuracy, ability to obtain biopsy samples, and direct visualization of tuberculous lesions have significantly improved the diagnostic process, leading to timely and precise identification of the disease. Furthermore, laparoscopy enables targeted therapeutic interventions, optimizing the effectiveness of anti-tubercular drugs and enhancing treatment outcomes. With its minimally invasive nature, laparoscopy also promotes faster recovery and improved patient comfort. As a revolutionary diagnostic and therapeutic approach, laparoscopy has paved the way for better management of peritoneal tuberculosis, contributing to enhanced patient care and outcomes in the field of tuberculosis medicine.
Similar Videos