The Rise of Robotic Surgery: Unlocking Advantages in Healthcare
Introduction:
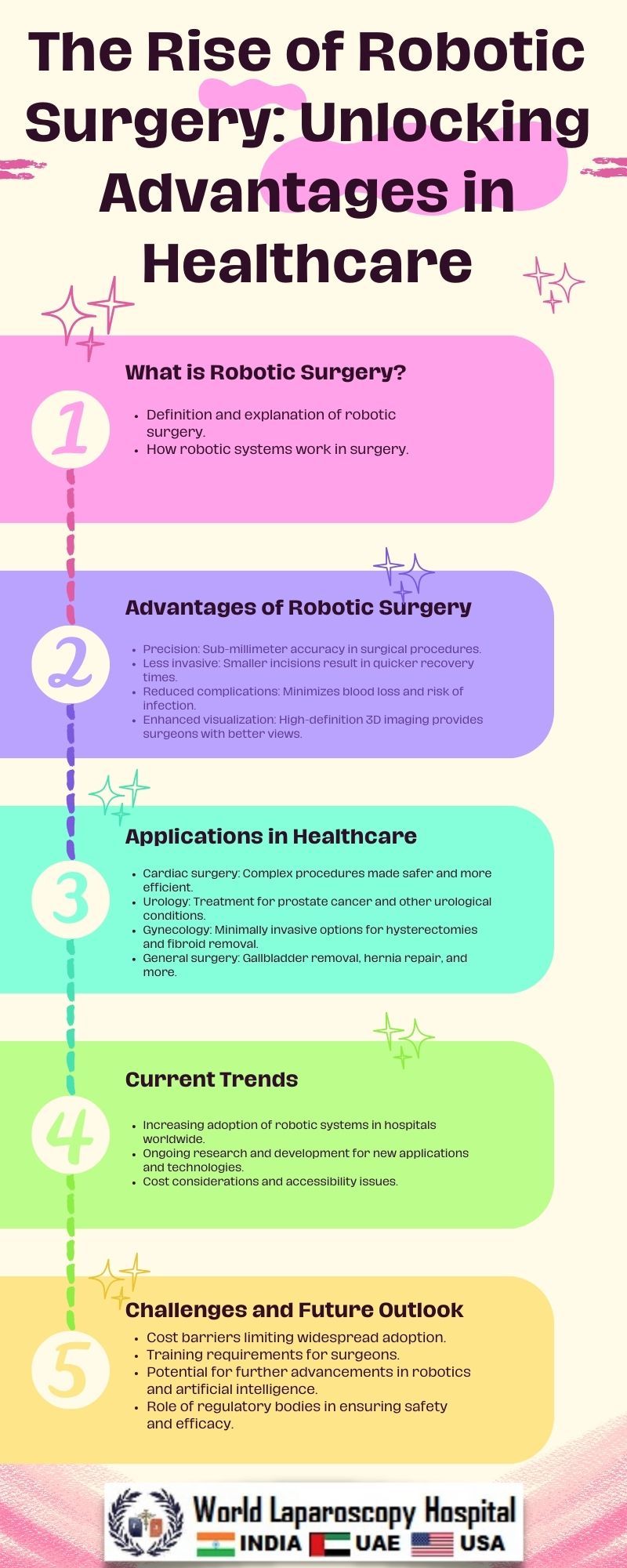
In recent years, the healthcare industry has witnessed a remarkable evolution with the integration of robotic technology into surgical procedures. Robotic surgery has transformed the way surgeries are performed, offering a plethora of advantages over traditional methods. This article explores the rise of robotic surgery, its benefits, challenges, and the future implications for healthcare.
Evolution of Robotic Surgery:
Robotic surgery traces its roots back to the 1980s when the first robotic system, the PUMA 560, was introduced for neurosurgical procedures. However, it wasn't until the late 1990s that the da Vinci Surgical System emerged as a game-changer in the field. Developed by Intuitive Surgical, the da Vinci System provided surgeons with enhanced capabilities, including improved visualization, dexterity, and precision.
Advantages of Robotic Surgery:
Robotic surgery offers numerous advantages over traditional open and laparoscopic techniques. One of the key benefits is enhanced precision, facilitated by the system's high-definition 3D imaging and wristed instruments that mimic the movements of the human hand with greater accuracy. This precision translates into reduced trauma to surrounding tissues, resulting in smaller incisions, less blood loss, and faster recovery times for patients.
Furthermore, robotic surgery enables surgeons to access hard-to-reach anatomical locations with greater ease, making it particularly beneficial for procedures in confined spaces or areas with delicate structures. The minimally invasive nature of robotic surgery also reduces the risk of postoperative complications such as infections and hernias, leading to improved patient outcomes and satisfaction.
Another advantage of robotic surgery is its potential to shorten hospital stays and recovery periods. By minimizing tissue damage and intraoperative bleeding, patients undergoing robotic procedures often experience less pain and require fewer pain medications. This, coupled with faster mobilization and rehabilitation, allows patients to return to their daily activities sooner, enhancing overall quality of life.
Challenges and Limitations:
Despite its many advantages, robotic surgery is not without its challenges and limitations. One of the primary concerns is the high cost associated with acquiring and maintaining robotic systems, which can pose financial barriers for healthcare institutions. Additionally, there is a steep learning curve for surgeons transitioning to robotic techniques, requiring extensive training and practice to master the technology effectively.
Another challenge is the lack of tactile feedback experienced by surgeons during robotic procedures. Unlike traditional surgery, where tactile sensation provides important cues about tissue characteristics and instrument manipulation, robotic systems rely solely on visual and auditory feedback, potentially increasing the risk of inadvertent tissue damage or complications.
Moreover, the reliance on advanced technology introduces the risk of technical failures or malfunctions during surgery, which could have serious consequences for patient safety. To mitigate these risks, stringent protocols and quality assurance measures must be implemented to ensure the reliability and performance of robotic systems.
Future Implications:
Despite these challenges, the future of robotic surgery appears promising, with ongoing advancements in technology and surgical techniques. As robotic systems become more compact, versatile, and affordable, their adoption is expected to increase across a broader range of surgical specialties and procedures.
Furthermore, emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and augmented reality (AR) hold the potential to further enhance the capabilities of robotic surgery. AI algorithms can analyze large volumes of medical data to provide real-time guidance and decision support to surgeons, improving surgical accuracy and outcomes. Meanwhile, AR overlays digital information onto the surgeon's field of view, enabling better anatomical visualization and surgical planning.
Conclusion:
Robotic surgery has emerged as a transformative force in modern healthcare, offering unparalleled precision, minimally invasive techniques, and improved patient outcomes. While challenges remain, ongoing technological advancements and innovations continue to expand the scope and effectiveness of robotic surgery across various medical specialties. As the field continues to evolve, robotic surgery is poised to play an increasingly integral role in shaping the future of healthcare delivery.
