Robotic Surgery: Enhancing Precision in Delicate Procedures
Introduction:
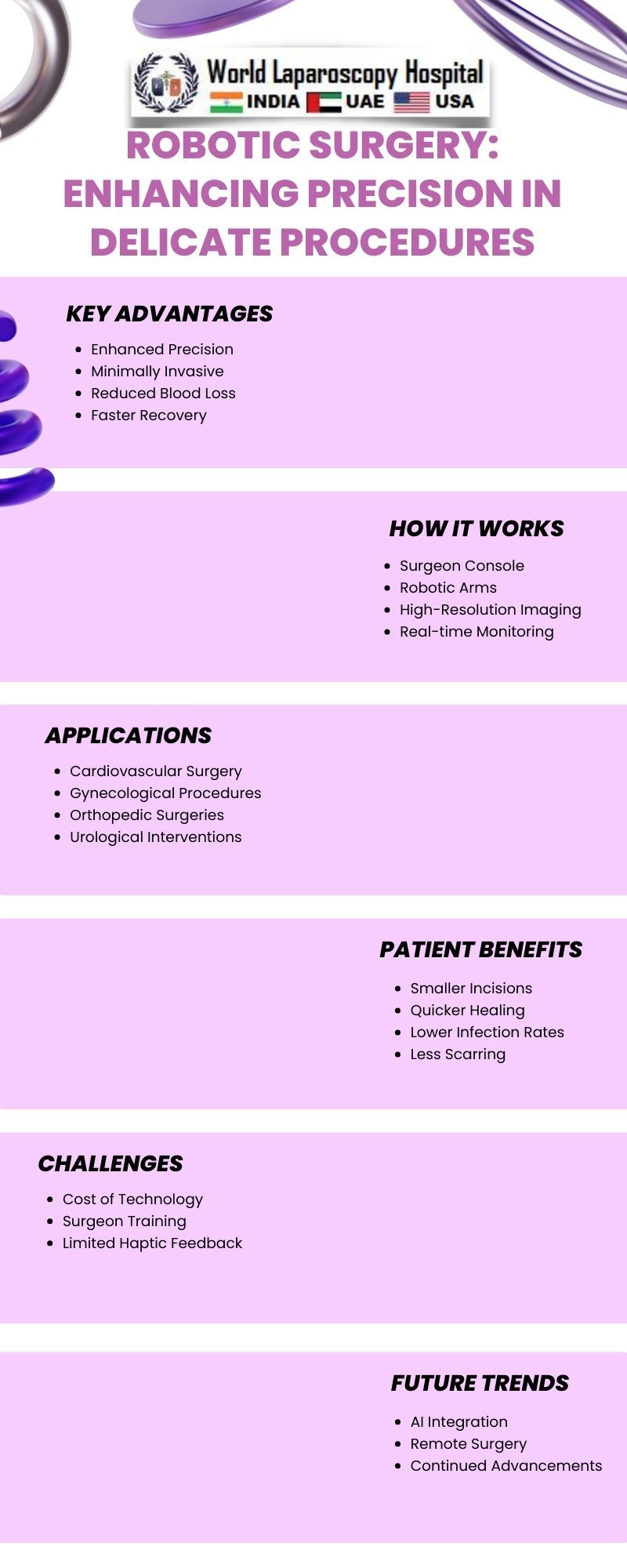
In the realm of modern medicine, robotic surgery stands as a groundbreaking innovation, significantly enhancing precision in delicate procedures. This technological advancement has transformed the landscape of surgical practices, offering unparalleled benefits in terms of accuracy, minimally invasive approaches, and improved patient outcomes.
The Evolution of Robotic Surgery:
Historical Perspective:
The roots of robotic surgery can be traced back to the early 20th century when the concept of telepresence and remote surgery began to take shape. However, it wasn't until the late 20th century that technological advancements paved the way for the development of sophisticated robotic surgical systems.
Emergence of da Vinci Surgical System:
The da Vinci Surgical System, introduced in the early 2000s, marked a significant milestone in robotic surgery. Developed by Intuitive Surgical, this system provided surgeons with a console to control robotic arms equipped with surgical instruments, offering a more precise and minimally invasive alternative to traditional procedures.
Precision and Control in Robotic Surgery:
Mechanism of Robotic Systems:
Robotic surgical systems employ a combination of robotic arms, cameras, and surgical instruments. The surgeon operates the system from a console, where hand movements are translated into precise movements of the robotic arms. The incorporation of high-definition cameras provides a 3D view of the surgical site, enhancing the surgeon's visibility.
Advantages of Enhanced Precision:
Minimally Invasive Procedures:Robotic surgery enables minimally invasive procedures through smaller incisions compared to traditional open surgeries. This not only reduces scarring but also minimizes blood loss, lowers the risk of infection, and accelerates postoperative recovery.
Improved Dexterity:The robotic arms used in surgery mimic the natural movements of the human hand but with enhanced dexterity. Surgeons can perform intricate maneuvers with greater precision, facilitating procedures that demand meticulous control, such as microsurgery and delicate tissue manipulation.
Enhanced Visualization:The incorporation of high-definition cameras provides surgeons with a detailed and magnified view of the surgical site. This heightened visualization allows for more accurate identification of anatomical structures, reducing the risk of errors and complications during surgery.
Applications of Robotic Surgery in Delicate Procedures:
Cardiovascular Surgery:
Robotic surgery has found its application in cardiovascular procedures, including coronary artery bypass grafting and mitral valve repair. The precision offered by robotic systems is crucial in these delicate surgeries, where the manipulation of tiny vessels and intricate cardiac structures is required.
Neurosurgery:
In neurosurgical procedures, where precision is paramount, robotic surgery has emerged as a valuable tool. Surgeons can navigate through intricate neural pathways with enhanced accuracy, making it particularly beneficial in tumor resections, epilepsy surgeries, and deep brain stimulation procedures.
Gynecological Procedures:
Gynecological surgeries, such as hysterectomies and ovarian cyst removals, have witnessed a shift towards robotic-assisted techniques. The minimally invasive nature of robotic surgery in gynecology reduces postoperative pain, shortens hospital stays, and allows for a quicker return to normal activities.
Urological Surgery:
Robotic surgery has become integral in urological procedures like prostatectomies and kidney surgeries. The precision offered by robotic systems is crucial when dealing with delicate structures like the prostate or intricate vascular networks in renal surgeries.
IV. Challenges and Future Directions:
Learning Curve for Surgeons:
Despite the numerous advantages, the adoption of robotic surgery comes with a learning curve for surgeons. Training programs and simulation technologies are being developed to facilitate the transition from traditional to robotic-assisted techniques, ensuring competence and proficiency among medical professionals.
Cost Considerations:
The initial investment and maintenance costs associated with robotic surgical systems can be a significant barrier for healthcare institutions. As technology evolves, efforts are being made to make these systems more cost-effective, ensuring wider accessibility and integration into healthcare settings.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence:
The future of robotic surgery is closely intertwined with the integration of artificial intelligence (AI). AI algorithms can assist surgeons by providing real-time data analysis, predictive modeling, and decision support, further enhancing precision and efficiency in delicate procedures.
Conclusion:
Robotic surgery has emerged as a transformative force in the field of medicine, offering unprecedented precision in delicate procedures. As technology continues to evolve and barriers are addressed, the widespread adoption of robotic surgical systems holds the promise of improving patient outcomes, reducing recovery times, and redefining the possibilities of modern surgical practices. The journey from early concepts to the current state of robotic surgery exemplifies the relentless pursuit of precision and innovation in the quest for optimal patient care.
