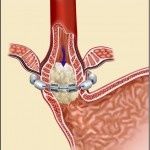
LINX Surgery for GERD
The LINX System is a small flexible band of interlinked titanium beads with magnetic cores. The magnetic attraction between the beads helps the LOS resist opening to gastric pressures, preventing reflux from the stomach into the oesophagus. Swallowing forces temporarily break the magnetic bond, allowing food and liquid to pass The Linx device opening to allow swallowing of foodnormally into the stomach. Magnetic attraction closes the LOS immediately after swallowing, restoring the body’s natural barrier to reflux. The LINX Reflux Surgery Procedure The LINX procedure is performed by minimally invasive laparoscopic (keyhole) surgery and takes less than an hour. The device is placed around the oesophagus, just above the stomach, in the area of the Lower Oesophageal Sphincter. Once in place, the LINX System begins to work immediately.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. GERD is characterized by the backflow of stomach contents into the oesophagus, causing symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, and difficulty swallowing. The current standard of care for GERD is medical therapy with proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or histamine receptor antagonists (H2RAs). However, surgical intervention may be necessary in patients who do not respond to medical therapy or who experience significant side effects from PPIs or H2RAs. LINX surgery is a minimally invasive surgical option for the treatment of GERD. In this essay, we will explore the mechanism of action, clinical outcomes, and potential benefits and risks of LINX surgery for GERD.
Mechanism of Action
LINX surgery involves the placement of a small, flexible band of magnetic beads around the lower oesophageal sphincter (LES), the ring of muscle that separates the oesophagus from the stomach. The magnetic beads are held together by a titanium wire, forming a ring that allows food and liquid to pass into the stomach but prevents the backflow of stomach contents into the oesophagus. The magnetic attraction between the beads helps to keep the LES closed, even during periods of increased pressure in the stomach, such as after eating.
The LINX device is designed to be a permanent implant, but it can be removed if necessary. The device is compatible with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and does not interfere with airport security screening.
Clinical Outcomes
Several studies have evaluated the safety and efficacy of LINX surgery for GERD. The results of these studies have been promising, with high rates of symptom improvement and patient satisfaction.
A randomized controlled trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2013 compared the safety and efficacy of LINX surgery to medical therapy with PPIs in patients with GERD. The study included 100 patients who were randomly assigned to receive either LINX surgery or medical therapy. The researchers reported that patients who underwent LINX surgery had significantly greater improvements in GERD symptoms, as measured by the GERD Health-Related Quality of Life questionnaire, compared to patients who received medical therapy. Patients who underwent LINX surgery also reported greater reductions in the use of PPIs and greater improvements in oesophageal acid exposure compared to patients who received medical therapy. The researchers reported no major complications or adverse events in either group.
A systematic review and meta-analysis published in the Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery in 2020 evaluated the safety and efficacy of LINX surgery for GERD. The review included 17 studies with a total of 1,244 patients. The researchers reported that LINX surgery was associated with a significant improvement in GERD symptoms, as measured by the Reflux Symptom Index and the GERD Health-Related Quality of Life questionnaire. The researchers also reported a significant reduction in the use of PPIs following LINX surgery. The most common complications associated with LINX surgery were dysphagia (difficulty swallowing) and bloating, but these complications were usually mild and resolved over time.
Potential Benefits and Risks
LINX surgery offers several potential benefits for patients with GERD, including:
Improved symptom control: LINX surgery has been shown to significantly improve GERD symptoms, such as heartburn, regurgitation, and difficulty swallowing.
Reduced need for medication: LINX surgery has been shown to significantly reduce the use of PPIs and H2RAs, which can have significant side effects with long-term use.
Minimal side effects: LINX surgery is a minimally invasive procedure that is associated with fewer side effects than traditional surgical procedures for GERD.
However, there are also some potential risks associated with LINX surgery, including:
Dysphagia: Dysphagia is a common side effect of LINX surgery, occurring in up to 20% of patients. This side effect is usually mild and resolves over time, but in some cases, it may require additional intervention.
Device-related complications: Device-related complications, such as device erosion or migration, may occur in a small number of patients. These complications may require additional surgical intervention to remove or replace the device.
Limited data on long-term outcomes: While the short-term outcomes of LINX surgery have been promising, there is limited data on the long-term outcomes of this procedure. Further research is needed to determine the durability of symptom improvement and the long-term safety of the device.
Conclusion
LINX surgery is a minimally invasive surgical option for the treatment of GERD. The mechanism of action of the device involves the placement of a small, flexible band of magnetic beads around the LES, allowing food and liquid to pass into the stomach while preventing the backflow of stomach contents into the oesophagus. The clinical outcomes of LINX surgery have been promising, with high rates of symptom improvement and patient satisfaction. However, there are also potential risks associated with this procedure, including dysphagia and device-related complications. Further research is needed to determine the long-term outcomes and safety of the device. Overall, LINX surgery is a promising option for patients with GERD who do not respond to medical therapy or who experience significant side effects from PPIs or H2RAs.
Top
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. GERD is characterized by the backflow of stomach contents into the oesophagus, causing symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, and difficulty swallowing. The current standard of care for GERD is medical therapy with proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or histamine receptor antagonists (H2RAs). However, surgical intervention may be necessary in patients who do not respond to medical therapy or who experience significant side effects from PPIs or H2RAs. LINX surgery is a minimally invasive surgical option for the treatment of GERD. In this essay, we will explore the mechanism of action, clinical outcomes, and potential benefits and risks of LINX surgery for GERD.
Mechanism of Action
LINX surgery involves the placement of a small, flexible band of magnetic beads around the lower oesophageal sphincter (LES), the ring of muscle that separates the oesophagus from the stomach. The magnetic beads are held together by a titanium wire, forming a ring that allows food and liquid to pass into the stomach but prevents the backflow of stomach contents into the oesophagus. The magnetic attraction between the beads helps to keep the LES closed, even during periods of increased pressure in the stomach, such as after eating.
The LINX device is designed to be a permanent implant, but it can be removed if necessary. The device is compatible with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and does not interfere with airport security screening.
Clinical Outcomes
Several studies have evaluated the safety and efficacy of LINX surgery for GERD. The results of these studies have been promising, with high rates of symptom improvement and patient satisfaction.
A randomized controlled trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2013 compared the safety and efficacy of LINX surgery to medical therapy with PPIs in patients with GERD. The study included 100 patients who were randomly assigned to receive either LINX surgery or medical therapy. The researchers reported that patients who underwent LINX surgery had significantly greater improvements in GERD symptoms, as measured by the GERD Health-Related Quality of Life questionnaire, compared to patients who received medical therapy. Patients who underwent LINX surgery also reported greater reductions in the use of PPIs and greater improvements in oesophageal acid exposure compared to patients who received medical therapy. The researchers reported no major complications or adverse events in either group.
A systematic review and meta-analysis published in the Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery in 2020 evaluated the safety and efficacy of LINX surgery for GERD. The review included 17 studies with a total of 1,244 patients. The researchers reported that LINX surgery was associated with a significant improvement in GERD symptoms, as measured by the Reflux Symptom Index and the GERD Health-Related Quality of Life questionnaire. The researchers also reported a significant reduction in the use of PPIs following LINX surgery. The most common complications associated with LINX surgery were dysphagia (difficulty swallowing) and bloating, but these complications were usually mild and resolved over time.
Potential Benefits and Risks
LINX surgery offers several potential benefits for patients with GERD, including:
Improved symptom control: LINX surgery has been shown to significantly improve GERD symptoms, such as heartburn, regurgitation, and difficulty swallowing.
Reduced need for medication: LINX surgery has been shown to significantly reduce the use of PPIs and H2RAs, which can have significant side effects with long-term use.
Minimal side effects: LINX surgery is a minimally invasive procedure that is associated with fewer side effects than traditional surgical procedures for GERD.
However, there are also some potential risks associated with LINX surgery, including:
Dysphagia: Dysphagia is a common side effect of LINX surgery, occurring in up to 20% of patients. This side effect is usually mild and resolves over time, but in some cases, it may require additional intervention.
Device-related complications: Device-related complications, such as device erosion or migration, may occur in a small number of patients. These complications may require additional surgical intervention to remove or replace the device.
Limited data on long-term outcomes: While the short-term outcomes of LINX surgery have been promising, there is limited data on the long-term outcomes of this procedure. Further research is needed to determine the durability of symptom improvement and the long-term safety of the device.
Conclusion
LINX surgery is a minimally invasive surgical option for the treatment of GERD. The mechanism of action of the device involves the placement of a small, flexible band of magnetic beads around the LES, allowing food and liquid to pass into the stomach while preventing the backflow of stomach contents into the oesophagus. The clinical outcomes of LINX surgery have been promising, with high rates of symptom improvement and patient satisfaction. However, there are also potential risks associated with this procedure, including dysphagia and device-related complications. Further research is needed to determine the long-term outcomes and safety of the device. Overall, LINX surgery is a promising option for patients with GERD who do not respond to medical therapy or who experience significant side effects from PPIs or H2RAs.