Cornual maternity takes place at the funnel-shaped location in the top uterine body that receives the insertion of the Fallopian tubes, the cornual region of the womb. Its occurrence price ranges from 1/2500 to 1/5000 live births and also represents 1% of ectopic pregnancies.
The incidence of heterotopic pregnancy with extrauterine gestation situated in the cornual location is not known, nonetheless, the incidence of cornual heterotopic maternity is approximated to be 1/3600 IVF pregnancies. We present one situation of spontaneous cornual heterotopic pregnancy diagnosed by ultrasound and also handled by laparoscopic-guided methotrexate shot into the cornual sac.
Heterotopic pregnancy represents an intrauterine gestational sac in the visibility of an ectopic pregnancy. It is an extremely unusual occurrence in spontaneous pregnancy however its incidence has raised with making use of assisted reproductive methods, being recognized in as much as 1% of these instances. The occurrence of cornual heterotopic maternity is unidentified; however, the incidence of heterotopic pregnancy itself has increased via using assisted reproductive innovations, and also most cornual heterotopic pregnancies happen after assisted reproductive technologies make use of. These situations have actually been treated commonly utilizing exploratory laparotomy and also cornual wedge resection with great outcomes. With developments in minimally invasive medical strategies, laparoscopic resection of cornual heterotopic pregnancies has been shown to be safe and viable.
Robotic resection of a cornual heterotopic pregnancy can be executed with minimal blood loss by using the "purse-string" suturing strategy in settings where vasopressin can not be made use of for hemostasis. This method consists of using a 2-0 V-Loc suture in a circumferential fashion around the ectopic pregnancy, which permits faster suturing as well as instant tension at the myometrium. The very same suture is then utilized to close the flaw, which allows for a simpler and efficient closure with marginal entry into the myometrium.
We demonstrate the effective da Vinci Robotic resection of cornual heterotopic pregnancy making use of a "purse-string" surgical technique. This method allows for very little blood loss in cases where extra techniques for hemostasis can not be made use of, such as injection of vasopressin and also uterine artery ligation.
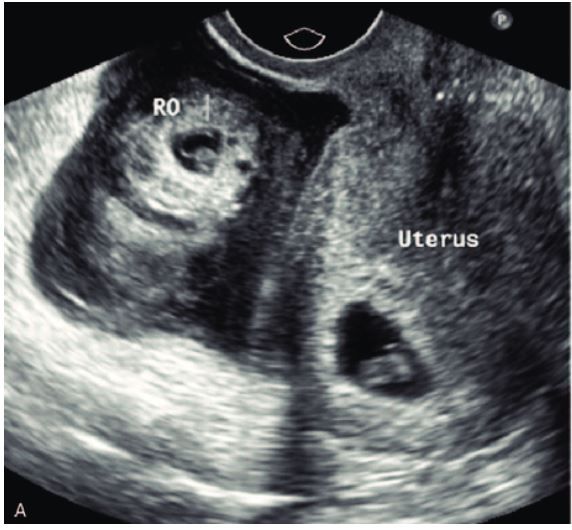
Cornual heterotopic ectopic pregnancy (CHEP) is a rare type of ectopic pregnancy that occurs when a fertilized egg implants in the cornual portion of the fallopian tube. This type of ectopic pregnancy is associated with a high risk of rupture and hemorrhage and requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. Minimally invasive surgical management of CHEP has become increasingly common in recent years, offering several potential benefits over traditional open surgery. This essay will explore the diagnosis and management of CHEP and the role of minimally invasive surgical techniques in its treatment.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of CHEP can be challenging due to its rarity and the lack of specific symptoms. However, early diagnosis is critical for reducing the risk of rupture and hemorrhage. Common presenting symptoms of CHEP include abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, and positive pregnancy test. Ultrasound imaging is the primary diagnostic tool for CHEP, although it may not always be able to differentiate between a cornual ectopic pregnancy and an interstitial ectopic pregnancy. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can also be used to confirm the diagnosis and provide more detailed information about the location and size of the pregnancy.
Management
The management of CHEP typically involves surgical intervention to remove the ectopic pregnancy and preserve the fallopian tube. Traditional open surgery, such as cornuotomy or cornual resection, has been the standard of care for many years. However, minimally invasive surgical techniques, such as laparoscopic and robotic surgery, have become increasingly common in recent years and offer several potential benefits over open surgery.
Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive surgical technique that involves making small incisions in the abdomen and using a laparoscope to visualize the surgical site. Laparoscopic surgery has several potential advantages over traditional open surgery for CHEP, including reduced postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times.
Laparoscopic surgery for CHEP typically involves the use of a trocar to access the abdominal cavity and the insertion of a laparoscope and other surgical instruments through small incisions in the abdomen. The cornual ectopic pregnancy is then visualized and removed using specialized instruments. The fallopian tube is typically preserved, although in some cases, it may be necessary to remove a portion of the tube to prevent future ectopic pregnancies.
Robotic Surgery
Robotic surgery is a newer minimally invasive surgical technique that involves the use of a robotic system to assist the surgeon in performing the surgery. Robotic surgery offers several potential advantages over laparoscopic surgery, including improved dexterity and visualization and reduced tremors.
Robotic surgery for CHEP is similar to laparoscopic surgery, but the surgeon uses a console to control the robotic arms and the laparoscope. The robotic system provides improved visualization and dexterity, which can be particularly useful for complex surgeries. Like laparoscopic surgery, robotic surgery for CHEP typically involves the removal of the cornual ectopic pregnancy while preserving the fallopian tube.
Comparison of Minimally Invasive Techniques
Several studies have compared the outcomes of laparoscopic and robotic surgery for CHEP. Overall, both techniques have been found to be safe and effective for the management of CHEP, with similar rates of successful pregnancy outcomes and low rates of complications. However, robotic surgery may offer some advantages over laparoscopic surgery, including reduced blood loss and shorter operating times.
In addition to these benefits, minimally invasive surgical techniques for CHEP can also provide improved cosmetic outcomes, as the small incisions used in these procedures result in less scarring than traditional open surgery. Minimally invasive surgery may also be associated with lower rates of postoperative complications, such as wound infection and hernia formation, although further research is needed to confirm these findings.
Despite the potential benefits of minimally invasive surgical techniques for CHEP, there are also several potential drawbacks that must be considered. One of the main concerns is the risk of damage to nearby structures, such as the ureter, bladder, and blood vessels, which can lead to serious complications. To minimize this risk, surgeons must have extensive training and experience in laparoscopic and robotic surgery and be familiar with the specific anatomy of the area.
Another challenge is the cost of minimally invasive surgical techniques, which can be higher than traditional open surgery. The cost of robotic surgery, in particular, can be significantly higher than laparoscopic surgery due to the need for specialized equipment and training.
Lastly, not all cases of CHEP may be amenable to minimally invasive surgical techniques. In some cases, open surgery may be necessary to safely remove the cornual ectopic pregnancy and preserve the fallopian tube.
Conclusion
Minimally invasive surgical techniques, such as laparoscopic and robotic surgery, have become increasingly common in the management of cornual heterotopic ectopic pregnancy. These techniques offer several potential benefits over traditional open surgery, including reduced postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times. However, the use of these techniques must be carefully considered in each individual case, taking into account the potential benefits and risks, the surgeon's experience and training, and the patient's individual needs and preferences. With proper training and experience, minimally invasive surgical techniques can provide safe and effective treatment for cornual heterotopic ectopic pregnancy and improve patient outcomes.